IUWMS v1 p111~
* Understanding Implications of Layer 2 and Layer 3 Roaming
:모바일 단말은 이동성을 제공하며 이동한 단말에 대한 인지를 해야 합니다.
이장에서는 로밍 가능한 최적 모델 설명합니다.
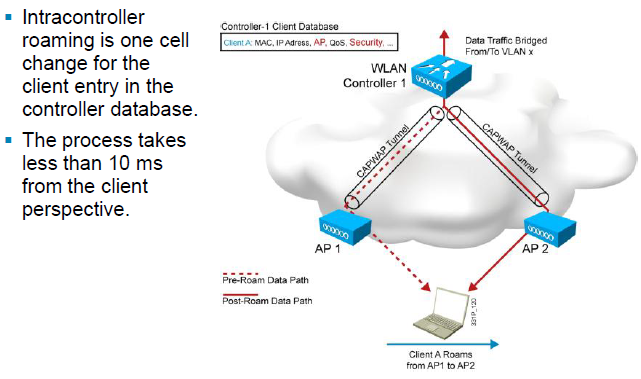
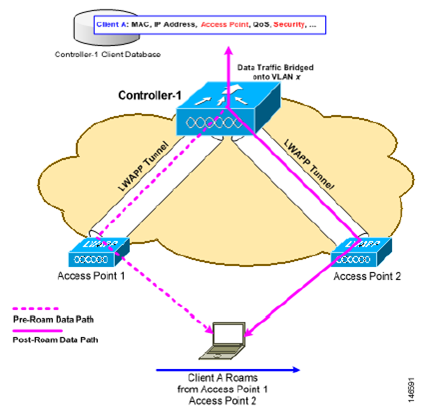
1.2.1 Mobility Overview (Mobility: Intracontroller Roaming)
: 1개의 컨트롤러에 join 된 AP들에 연결된 STA이 이동 할 경우, 10ms 이내 로밍 완료(Seamless Roaming)
: 컨트롤러에 저장되는 정보 "client MAC and IP addresses, security context and associations,
quality of service (QoS) contexts, wireless LANs (WLANs), and the associated access point"
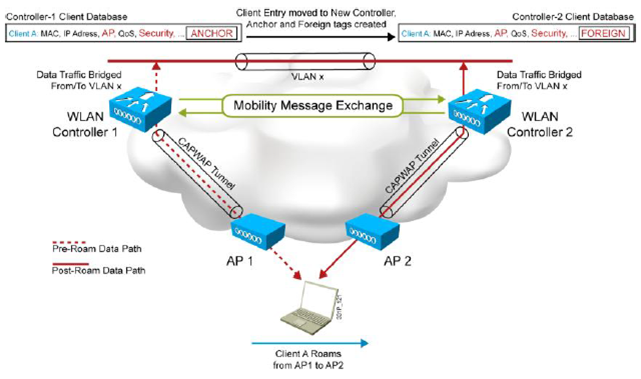
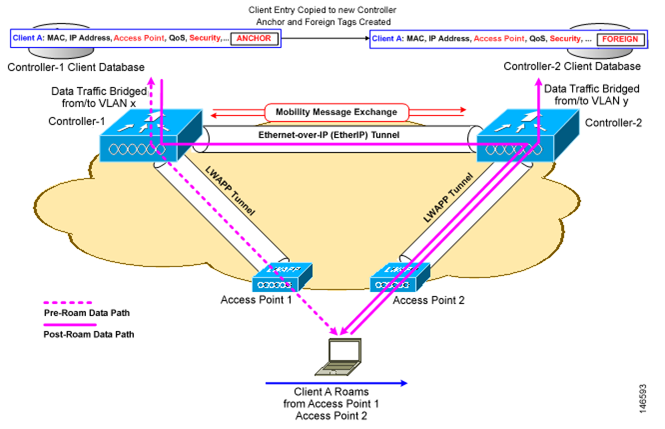
1.2.2 Intercontroller, Intrasubnet Roaming
: 1개 이상의 컨트롤러 간에 join 된 AP에 연결된 STA의 이동 시(동일한 서브넷에 STA이 위치 시)
: 컨트롤러간 Mobility 정보 교환, Anchor 와 Foreign 컨트롤러로 구성됨.
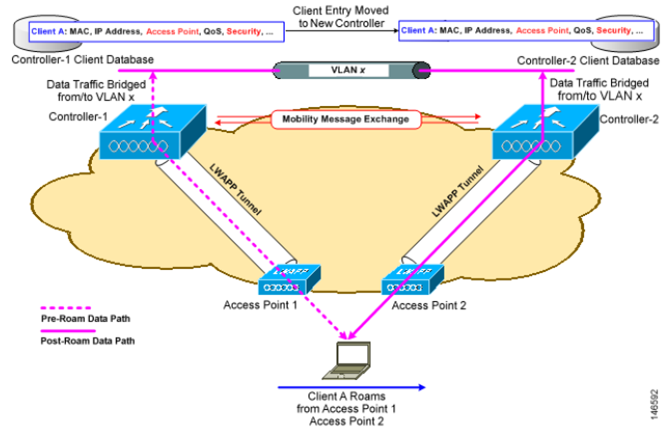
1.2.3 Intercontroller, Intersubnet (Symmetric) Roaming
: 1개 이상의 컨트롤러 간에 join 된 AP에 연결된 STA의 이동 시 (다른 서브넷에 STA이 위치 시)
: STA의 트래픽은 Anchor 컨트롤러를 통해서 대칭형 통신
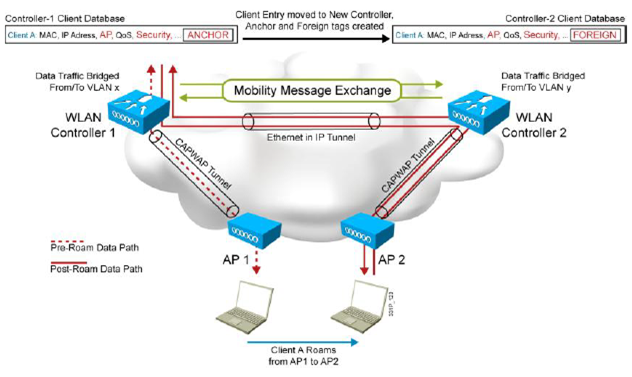
위 처럼 Asymmetric Tunneling 은 현재 시스코 무선 WLC에서 지원하지 않는다
1.2.4 Mobility Groups
: 같은 Mobility Group Name 을 같는 컨트롤러간에 STA은 seamless 로밍이 됨, 같은 Virtual Gateway IP addr.
: 같은 Mobility Group 간에는 client 정보, context 정보를 공유함
: mobility message 를 컨트롤러간 UDP 16666 을 통해서 교환함. IPsec 암호화 시 UDP 16667로 교환함.
: 컨트롤러 5.2 이상에서는 1개의 mobility group 에 24개의 컨트롤러 설정 가능.
: 동일한 mobility list(다른 mobility group names) 에 72개의 컨트롤러 설정 가능.
: Mobility Group 를 사용하여 로밍 제한도 가능함.
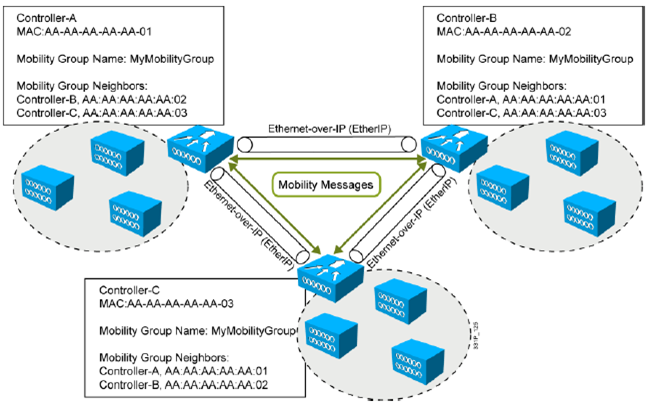
1.2.5 Mobility Groups and Mobility Lists
: Mobility Group : CCKM, PKC 를 유지
: Mobility List 같음, Mobility Gruop 다름 : fully authenticated 하지 않지만 IP는 유지
: List 의 경우 서로간에 다를 수 있음. 즉 C1->C2,C3 이며 C2->C1, C3->C1 이지만 C2<->C3 아닐 수 있음.
위 경우 C2와 C3간 STA는 seamless 로밍 되지 않음.
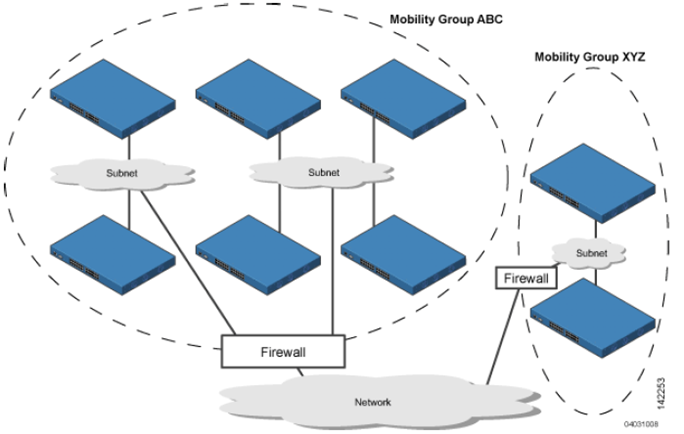

1.2.5.1 추가 : Mobility Domains = 여러 Mobility Group
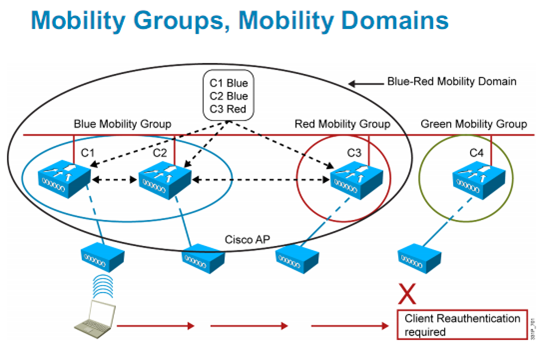
1.2.5.2 추가 : Mobility List = 여러 Mobility Group
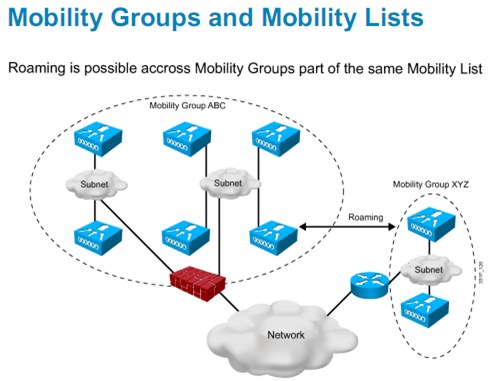
=> 결론은 여러 Mobility Group 은 하나의 Mobility List(=Mobility List) 에 속하며 로밍이 지원된다.
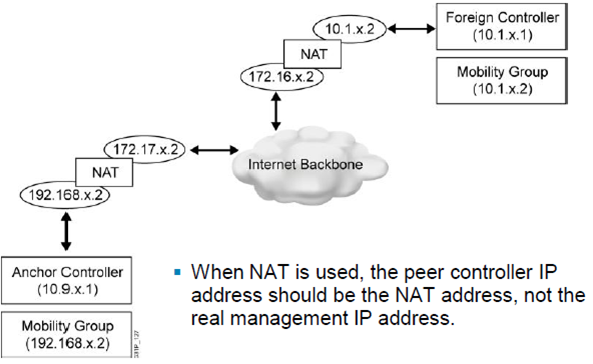
1.2.6. Mobility Groups and NAT(p119)
: NAT 환경에서 지원...
1.2.7 Configuring Mobility Groups
|
모든 컨트롤러에는 management interface 통신이 되야 합니다. 모든 컨트롤러는 동일한 virtual IP address 공유 해야 합니다. 모든 컨트롤러는 동일한 버전의 code를 실행 해야 합니다. UDP 포트 16666 및 16667는 이동성 교환을 위해 허용. (test, CLI mping) Mobility ping over UDP UDP 포트 5246 5247 CAPWAP 트래픽 (12222 및 LWAPP에 대 한 12223)에 대 한 허용 되어야 합니다. IP프로토콜 50(IP 압축) 및 IP프로토콜 97(IP 이더넷)를 허용.(test, eping) Mobility ping over Ethernet over IP(EoIP) UDP 포트 500을 허용 해야 합니다 secure mobility groups을 사용 하는 경우. |
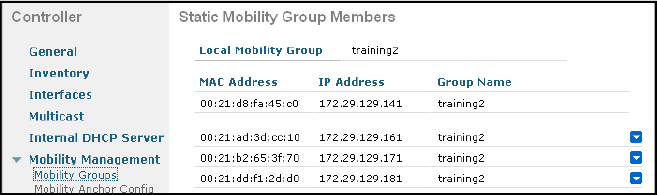
1.2.7.1 Configuring Mobility Groups (Cont.)
: LMG(training2) 가 setup 에서 설정한 내용이다. 컨트롤러 정보(mac, ip, group name)를 입력한다.
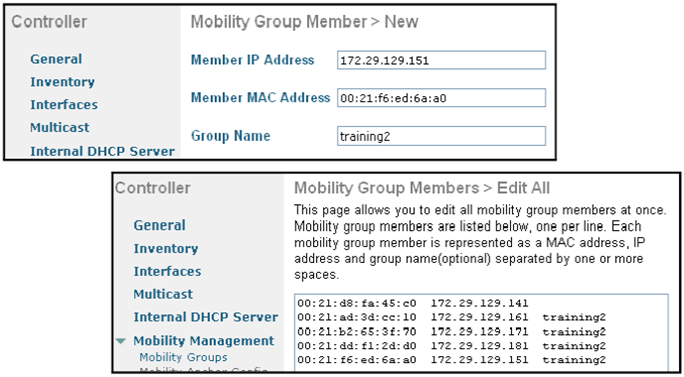
1.2.7.2 Intercontroller Messaging
: 컨트롤러간 Multicast 로 정보를 교환하려면 아래 설정을 해야 한다. 설정 없을 시 유니캐스트로 전달.
: Local Group MIP 주소 설정을 하며 만약 다른 MG 컨트롤러의 경우에 IP 지정 하지 않을 시 유니캐스트로 전달.
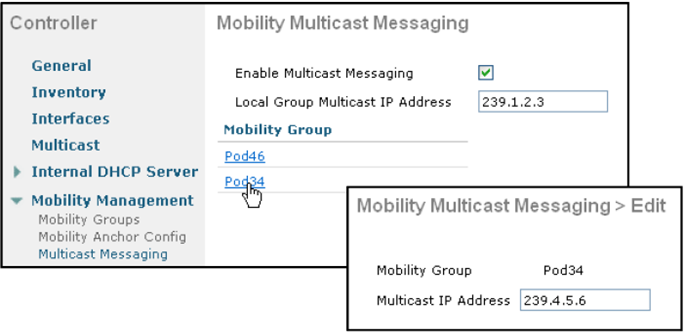
1.2.7.3 Mobility Recommended Practices
: 권고 내용
'DHCP Required' option can slow down roaming. <- STA 무선IP폰일 경우 문제 될 수 있음.
Use Multicast for Mobility whenever possible.
Use config mobility secure-mode to secure the tunnel.
<- (config) mobility secure-mode(16667로 통신), 단 2100 WLC, WLCM은 제공하지 않음.
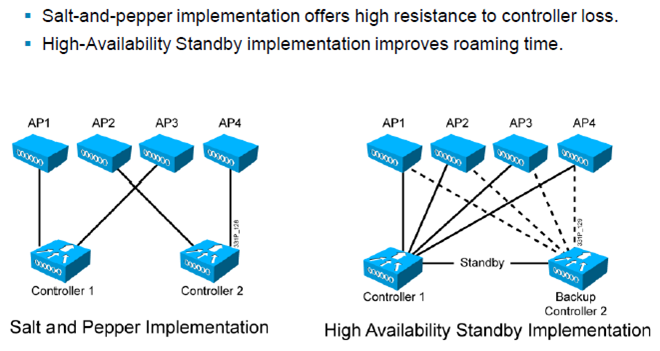
1.2.8 Minimize Intercontroller Roaming
: 소금과 후추 구성은 층별 컨트롤러에 AP를 차례차례로 join 한 구성
: HA Full standby 는 WLC1만 사용하다가 장애시 WLC2로 적용
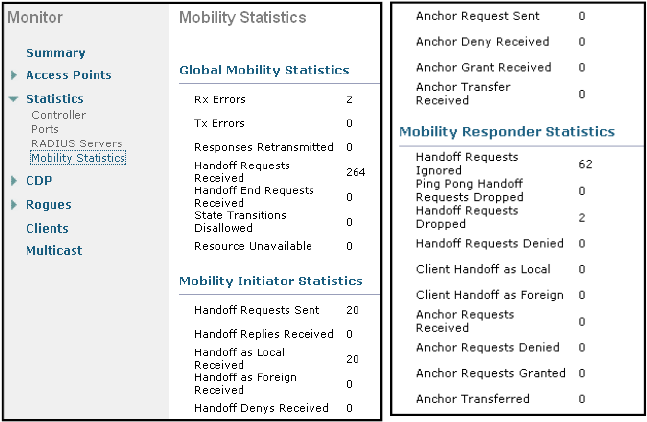
1.2.9 Monitoring Mobility (Monitor > Statistics > Mobility Statistics)
: CLI commands - show mobility {summary | anchor | statistics }
|
Global statistics: Affect all mobility transactions Mobility initiator statistics: Generated by the controller initiating a mobility event Mobility responder statistics: Generated by the controller responding to a mobility event |
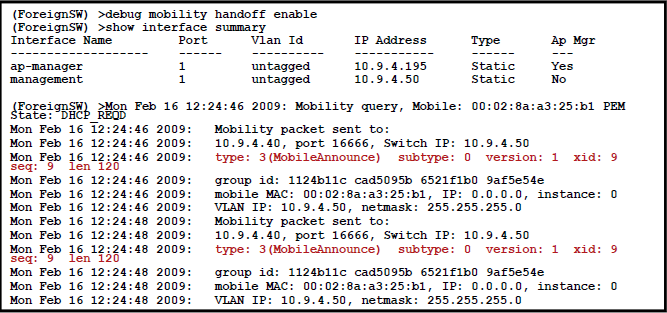
1.2.10 Debug of Mobility Session Establishment
: debug mobility {directory | handoff} {enable | disable}
================================
Cisco.Press.Deploying.and.Troubleshooting.Cisco.Wireless.LAN.Controllers.Nov.2009.pdf
Chapter 9: Mobility > Mobility Handoff Types(p235)
: 6개의 로밍 타입
1. Local to Local
2. Local to Foreign
3. Foreign to Local (1)
4. Foreign to Local (2)
5. Foreign to Foreign
6. Auto-Anchor
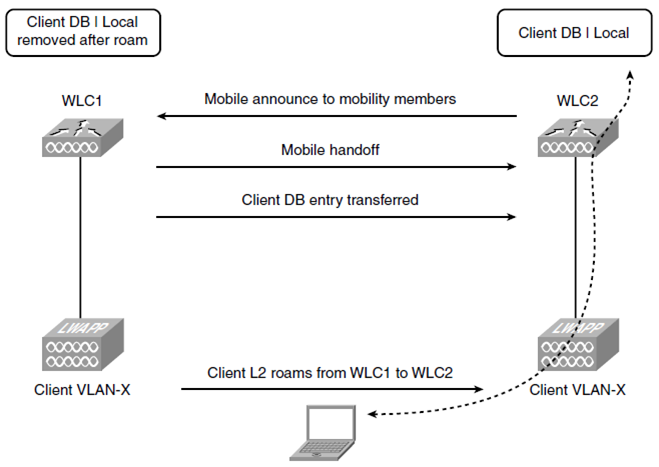
1. Local to Local
Local-to-Local Handoff 는 two controllers 간에 Layer 2 roam 일 때 입니다.
The client roams to an AP on WLC2, WLC2 sends a "Mobile Announce" to the mobility group members.
WLC1 responds with a "Mobile Handoff", and the client database entry is moved from WLC1 to WLC2.
WLC1 no longer has the client database entry.
WLC2 becomes the IP point of presence for the client.
2. Local to Foreign
A Local-to-Foreign Handoff occurs when the client performs a Layer 3 (inter-controller inter-subnet) roam
and requires only two packets. Layer3 로밍이며 다른 컨트롤러간에 다른 서브넷 환경에서 발생
When the client roams from WLC1 to WLC2, WLC2 sends a "Mobile Announce", and WLC1 responds with a "Mobile Handoff".
The client database entry is copied from WLC1 to WLC2.
WLC1 marks the client entry as Export Anchor, and WLC2 marks the client entry as Export Foreign.
The IP point of presence for the client remains WLC1.

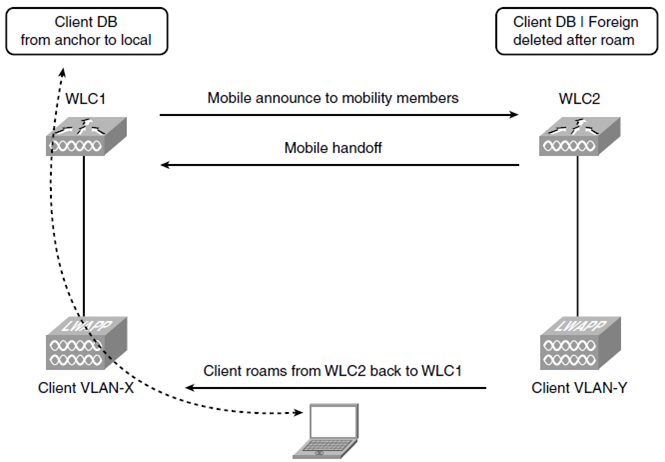
3. Foreign to Local (1)
위 2번 환경에서 무선 단말이 다시 Local WLC로 돌아올 경우
A Foreign-to-Local (1) Handoff is the opposite of the Local-to-Foreign Handoff and again requires only two packets.
The client is roaming from the foreign controller back to the anchor controller it came from.
shows that when the client roams back to WLC1, WLC1 sends out a Mobile Announce,
and WLC2 responds with a Mobile Handoff.
WLC1 knows it used to have a Local entry for that client and removes the Export Anchor designation
from the client entry and once again marks it as Local.
WLC2 deletes the database entry for the client. WLC1 remains the IP point of presence for the client.
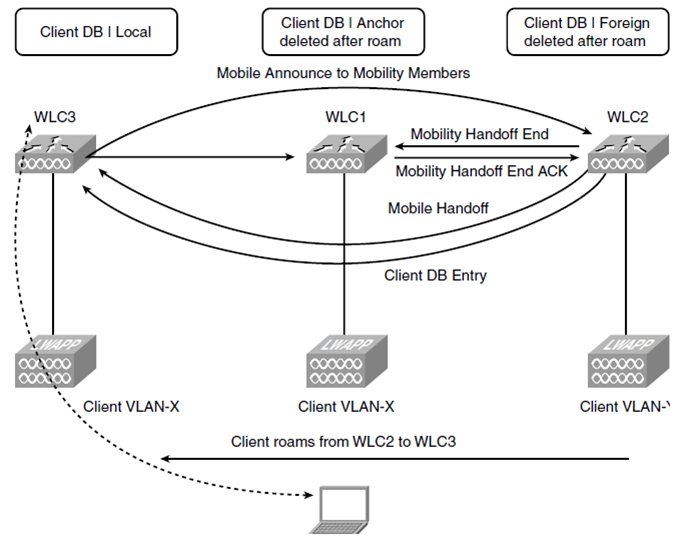
4. Foreign to Local (2)
Foreign-to-Local (2) Handoff 는 3개의 컨트롤러가 필요하다.
무선 단말은 Foreign WLC에서 3번째 WLC로 로밍한다.(단, Anchor WLC와 같은 Subnet)
WLC3은 Mobile Announce 를 Mobility Member(WLC2, WLC1?)에게 보낸다.
WLC2는 Client DB Entry 를 WLC3에게 전달하고 WLC1에게 Mobility Handoff End 를 전달한다.
이후 WLC1,2는 client database entry를 삭제한다. same subnet 이기 때문에 client DB를 WLC3이 point of presence 한다
The client roams from the foreign controller to a third controller whose WLAN is in the same subnet as the anchor controller.
When the client roams to WLC3, WLC3 sends out a Mobile Announce, and WLC2 responds with a Mobile Handoff.
The client database information is extracted from WLC2 by WLC3.
WLC2 sends a Mobility Handoff End, and WLC1 responds with a Mobility Handoff End ACK.
WLC1 and WLC2 delete the client database entry, and WLC3 marks the client entry as Local because
its WLAN is in the same subnet as the client IP and becomes the IP point of presence for the client.
5. Foreign to Foreign
Foreign-to-Foreign Handoffs 3개의 컨트롤러간에 발생(다른 서브넷 환경). 가장 복잡한 handoff transaction.
When the client roams to WLC3, WLC3 sends out a Mobile Announce to the mobility members.
WLC2 responds with a Mobile Handoff, and all client entry information is extracted from WLC2 and transferred to WLC3.
After sending the Mobile Handoff, WLC2 sends an Anchor Xfer message to the WLC1, at which time WLC1
responds with an Anchor Xfer ACK and sets up the new client forwarding path.
WLC2 then deletes the client session. WLC3 sends an Anchor Req message to WLC1, and WLC1 responds with an Anchor Grant message.
The IP point of presence for the client remains with WLC1.

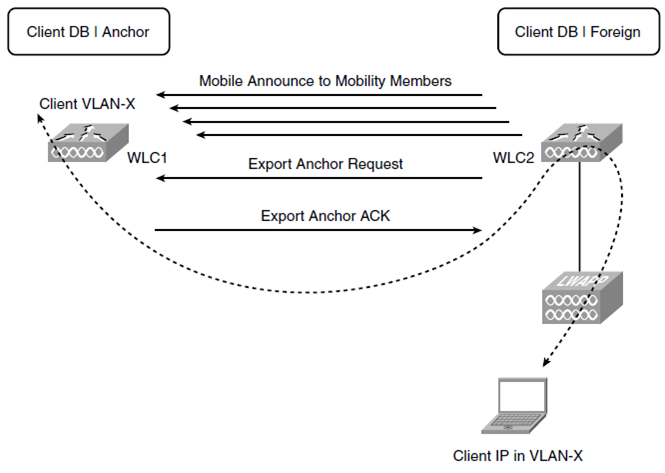
6. Auto-Anchor
auto-anchoring 설정 경우 동작이 조금 다르다.
로밍 시 WLC2는 "Mobile Announce" messages to the mobility members 보내지만 auto-anchor controller(WLC1)은 응답하지 않는다.
그러면 WLC는 Local entry 에 Client 정보를 만든다. WLC2는 "Export Anchor Request"를 보내고 WLC1은 "Export Anchor ACK"로 응답.
Client DB entry 는 anchor WLC에서 copy 된다.
After WLC2 sends the fourth Mobile Announce and does not receive a Mobile Handoff from any other controllers
in the mobility group, instead of creating a Local entry for the client, WLC2 sends an Export Anchor Request to WLC1,
which is configured as the autoanchor for the client WLAN.
The anchor controller responds with an Export Anchor ACK.
The client database entry is copied to the anchor controller.
WLC1 marks the client entry with Export Foreign, and WLC1 marks the entry as Export Anchor.
WLC1 is the IP point of presence for the client.
With the auto-anchoring scenario, you have a fixed anchor controller for the client WLAN that will never change.
The client will have an IP address in the same VLAN as the anchored WLAN interface on WLC1.
출처 : http://mongu2.blog.me/140156975013
'Legacy Skills > EPC' 카테고리의 다른 글
| GTP-C Interface (0) | 2014.03.20 |
|---|---|
| LTE Network Entity (0) | 2014.03.20 |
| LTE와 Wi-Fi 네트워크 연동 구조 (1편: Network Reference Model) (0) | 2014.03.20 |
| EPS (Evolved Packet System) - 1 (0) | 2014.03.20 |
| LTE의 GTP 터널 소개 (0) | 2014.03.11 |
댓글